User Tools
Sidebar
visual_sensory
**This is an old revision of the document!**
Table of Contents
Visual Sensory
Characteristics of visual sensory processing include: visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, color vision, and night vision.
Red light will not destroy rods' dark adaptation
When stimulated by light, rods rapidly lose their sensitivity, and it takes a long time for them to regain it (up to a half hour) once they are returned to the darkness.
Illuminating objects in red light in a dark environment will not destroy the rods’ dark adaptation. For example, on the bridge of a ship, the navigator may use a red lamp to stimulate cones to read the fine detail of a chart. This stimulation with red light will not destroy the rods’ dark adaptation and hence will not disrupt the ability of personnel to scan the horizon for faint lights or dark forms.
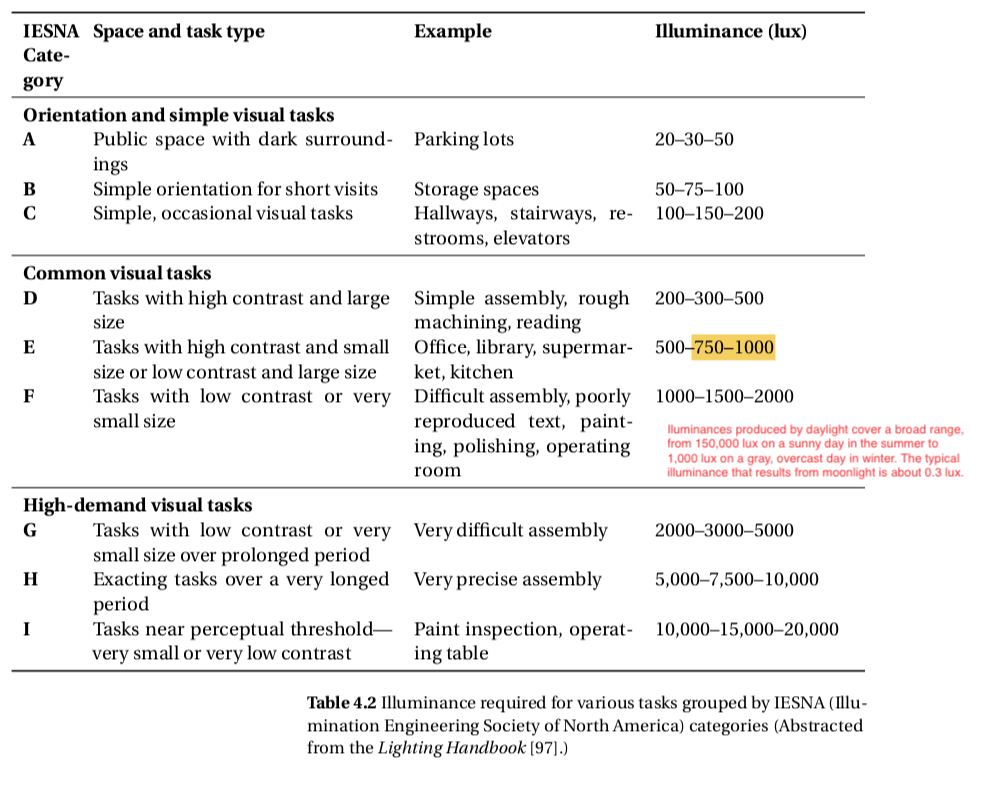
Illuminance (lux) and Brightness (nits)
- Illuminances produced by daylight cover a broad range, from 150,000 lux on a sunny day in the summer to 1,000 lux on a gray, overcast day in winter. The typical illuminance that results from moonlight is about 0.3 lux.
- Illuminance value for a typical home or office is between 300 to 500 lux (30 to 50 footcandles).
- Smartphone screen = ~500–2,000 nits (cd/m²) (1 nit = π lux ≈ 3.14 lux)
- Sunlight on a surface = ~100,000 nits
- A white wall lit by a 60W bulb = ~50–100 nits depending on distance
Can a 1000 nits smartphone screen be seen in a 3000 lux environment
visual_sensory.1755402387.txt.gz · Last modified: 2025/08/17 11:46 by admin
- _